Executive Summary
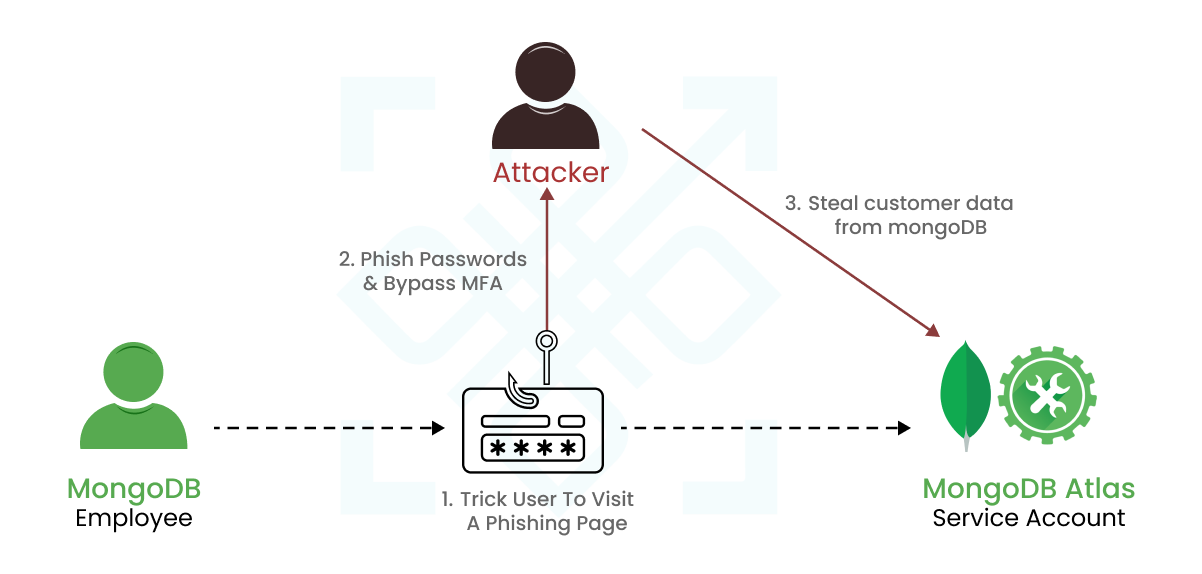
Snowflake an American cloud computing–based data cloud company, identified a breach in June 2024, which had far-reaching implications for various organisations. Attackers exploited stolen credentials from a Snowflake employee, enabling unauthorised access to sensitive customer data, including credentials and access tokens. This breach was exacerbated by bypassing Okta’s security measures, allowing the attackers to generate new session tokens and access extensive customer data without detection.
Key Affected Customers:
Attack Method
- Credentials Theft: Initial access through compromised employee credentials
- Bypass Mechanism: Circumvention of Okta Security Protocols
- Exploitation: Generation of new session tokens to access databases and steal data
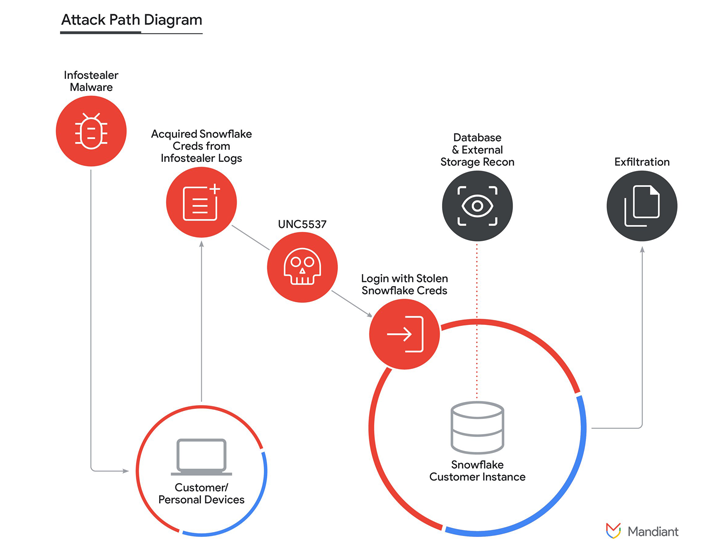
The Domino Effect
The Snowflake breach has created a domino effect, where the initial compromise has led to multiple subsequent breaches. This incident mirrors the earlier Okta breach,, where attackers leveraged stolen credentials to infiltrate various organizations.
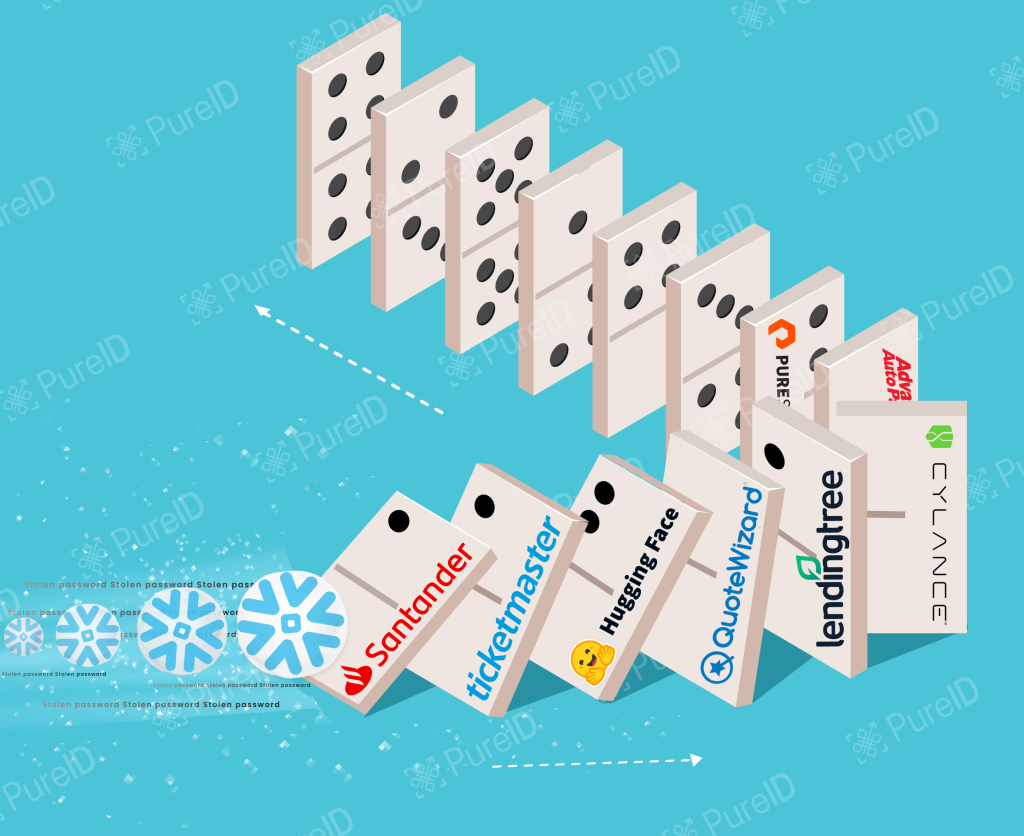

Companies affected include:
- Ticketmaster: Reported unauthorised access to sensitive data.
- Advance Auto Parts: Experienced data theft, with stolen information now for sale on dark web marketplaces.
- Santander Bank: Compromised customer data led to financial and reputational damage.
- Hugging Face, Quote Wizard, Lending Tree: Also reported breaches, with more organizations likely to follow .
Inherent Weaknesses in Traditional IAM Solutions
Password + MFA Based Authentication:
- Reliance on passwords makes systems vulnerable to phishing and credential theft.
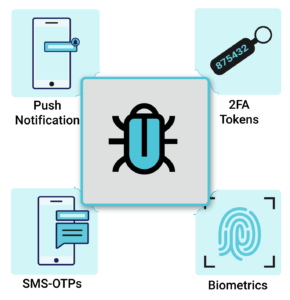
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is often ineffective as attackers can bypass Password + MFA protection mainly by phishing or using a compromised device.
- Social Engineering attacks have shown that phishing resistant MFA like FIDO keys, & passkeys can prove to be ineffective & can be easily disabled or reset.
IAM Blind Spots:
Apart from reliance on vulnerable passwords for identifying user. The existing IAM solutions are blind to following risks
- Connection Risk – Traditional IAM solutions lack visibility of user connections. They cannot know whether an authentication request is coming from an authorised actor or an attacker in the middle.
- User’s Device Risk – They also do not account for the type & security posture of user’s devices, leaving systems exposed to malware and remote monitoring, as seen in the Uber incident.
Impact Assessment
The Snowflake breach is termed as the biggest data breach so far and it’s cascading effect has led to numerous organisations reporting security incidents & data breach.
The amplification effect could potentially lead to a vast number of downstream breaches, escalating the overall impact.

Towards a Secure Future
Challenges with Current Solutions:
- Time and again Password + MFA based systems are proven to be ineffective against simple attacks like phishing & social engineering.
- There is a pressing need for more robust authentication mechanisms.
Protect your Enterprise, #GoPasswordless with PureAUTH
FIDO Solutions like Passkeys and hardware tokens focus on giving users a passwordless experience keeping the passwords on the server as the primary way to identify and authenticate users.
PureAUTH Platform on the other hand provides a comprehensive passwordless approach, eliminating the passwords from server side & not just from user side. PureAUTH is the only solution that protects an organisation against phishing, social engineering, frauds & all types of credential-based attack.
To learn more about PureAUTH & how it protects your existing IAM systems like Okta, OneLogin, CISCO Duo, or Azure AD in just 60 minutes at Zero Cost – get in touch with us