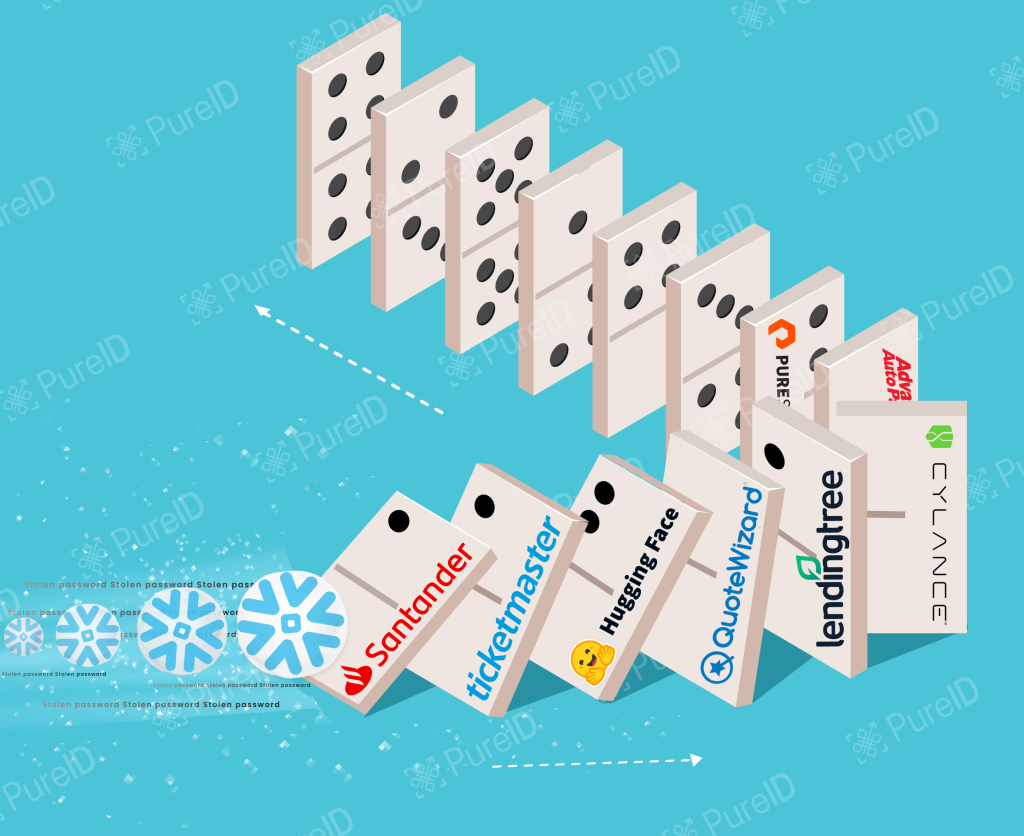
Introduction
The global cloud services market, valued at $551.8 billion in 2021, is projected to reach $2.5 trillion by 2031. This explosive growth makes cloud environments a prime target for cyber criminals. One such group is Storm-0501, an extortion-orientated cyber crime group that’s been conducting multi-stage attacks against hybrid cloud environments in government, manufacturing, transportation, and law enforcement. Since its inception in 2021, Storm-0501 has changed its operations, shifting from targeting U.S. school districts to running RaaS operations. This blog post explains the tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) of the group to help improve organizational defenses with mitigation strategies.
Storm-0501 TTPs: Steal Technique
Initial Compromise and Discovery
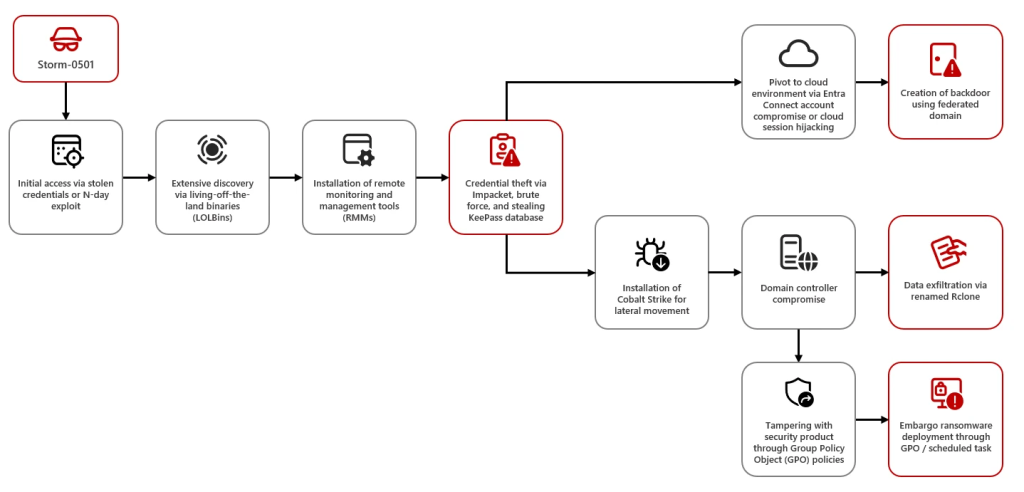
Storm-0501 has traditionally obtained initial access using compromised credentials or exploitation of known vulnerabilities in systems with widespread use. In a recent campaign, Storm-0501 exploited known vulnerabilities in Zoho, ManageEngine (CVE-2022-47966), Citrix, NetScaler (CVE-2023-4966), and ColdFusion (possibly CVE-2023-29300 or CVE-2023-38203). After gaining entry into the target network, it conducts extensive exploration using several tools to find high-value assets, obtain credentials, and increase privileges.
Lateral Movement and Credential Theft
Storm-0501 uses Impacket’s SecretsDump and Cobalt Strike to move laterally across the network grabbing credentials to compromise additional devices. They target the administrative accounts, mostly utilizing password reuse or weak credentials, accessing both their on-premises and cloud environments. Using cloud session hijacking, especially in Microsoft Entra, they establish persistent backdoor access into the target systems.
From Ground to Cloud: Storm-0501’s Cross-Environment Exploits
One of the most significant tactics Storm-0501 uses is the exploitation of the Microsoft Entra Connect Sync service by doing synchronization of credentials between the on-premises AD and cloud. The attackers escalate the privileges in both environments after compromising the sync accounts to have control over the cloud environment and for a persistent backdoor for the next attack.
Aftermath of the Storm-0501 Attack
The aftermath of a Storm-0501 attack can be devastating, with the group often gaining control over both on-prem and cloud environments, exfiltrating sensitive data, deploying ransomware, and tampering with security products to avoid detection. The threat will only increase with the new deployment of Embargo ransomware, where victim data is encrypted and sensitive information leaked unless a ransom is paid.
Such attacks would lead to the stealing of credentials, data breaches, service disruptions, and heavy financial losses. Storm-0501 pays extra attention to sensitive sectors such as hospitals, which raises stakes not only on data security but also public safety.
Mitigation
Hybrid Cloud Security Enhancement
While Microsoft has implemented restricted permissions on DSA roles in Entra Connect Sync and Entra Cloud Sync, defending Storm-0501 needs a robust, multi-layered approach. Conditional Access policy can further harden access to cloud services from non-verified devices and locations as a risk mitigation approach.
Harden Cloud Security Measures
Even solutions proposed by today’s market leaders such as Microsoft are still often based on passwords in most cases and, hence, would probably fail to deliver proper authentication in a much-enlarged, cloud-to-on-premises environment. Therefore, organizations should embrace solutions such as PureAUTH IAM Firewall that come with the strongest security and reliability against attacks exploiting credentials and even zero-day vulnerabilities. Built on a zero-trust architecture, it provides reliable, passwordless protection, further enhancing resilience against sophisticated threats.
Conclusion
Organizations need to move away from convenient and conventional IAM solutions and start interacting with leading edge defenses, such as passwordless authentication. Enhancing cloud security policies and infrastructure defenses will enable enterprises to withstand new cyber threats.
Solutions like PureAUTH will help organizations build a far more robust infrastructure that is not only adaptable but will also neutralize the most sophisticated cyber threats in existence.
Read Also
Microsoft Entra ID Vulnerabilities: Pass-Through Authentication Risks
Storm-0501: Ransomware attacks expanding to hybrid cloud environments
The achilles’ heel of cloud security: Why two-factor authentication isn’t enough