Connect with Us!
Subscribe to receive new blog post from PureID in your mail box

On July 1, 2024, the cybersecurity community was alerted to a significant vulnerability within OpenSSH, dubbed "regreSSHion" (CVE-2024-6387). This critical flaw, discovered by the Qualys Threat Research Unit (TRU), allows unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE) with root privileges on glibc-based Linux systems. The vulnerability, which affects the default configuration of OpenSSH's server (sshd), poses a severe security risk due to its potential for complete system compromise without user interaction.

RegreSSHion, tracked as CVE-2024-6387, is an unauthenticated RCE vulnerability in OpenSSH’s server (sshd). This flaw grants attackers full root access, making it a high-severity threat with a CVSS score of 8.1. The vulnerability affects versions 8.5p1 to 9.8p1 of OpenSSH, as well as versions earlier than 4.4p1 if not patched for previous vulnerabilities (CVE-2006-5051 and CVE-2008-4109). The issue arises from a signal handler race condition that can be exploited by failing to authenticate within a set time period (LoginGraceTime).
The Qualys TRU discovered that this vulnerability is a regression of a previously patched flaw, CVE-2006-5051, reported 18 years ago. A regression in this context means that a previously fixed issue has reappeared in a subsequent software release. This often occurs due to changes that inadvertently reintroduce the problem. The regression was introduced in October 2020 with OpenSSH version 8.5p1, highlighting the importance of thorough regression testing to prevent the reintroduction of known vulnerabilities.
The vulnerability involves a specific sequence of function calls and interactions between the signal handler and the main program logic. Here’s a breakdown of the critical components:
Function Call Chain:
Heap Allocation Issues:
Exploit Strategy:
The regreSSHion vulnerability impacts glibc-based Linux systems running vulnerable versions of OpenSSH. Exploitation of this flaw can result in complete system takeover, allowing attackers to execute arbitrary code with root privileges. The attacker leverages the predictable heap layout and timing to achieve arbitrary code execution:
Heap Layout Manipulation:
Signal Timing:
Arbitrary Code Execution:
While successful exploitation has been demonstrated under lab conditions, it typically requires 6-8 hours of continuous connections. This makes mass exploitation challenging but not impossible.
The vulnerability affects the following OpenSSH versions:
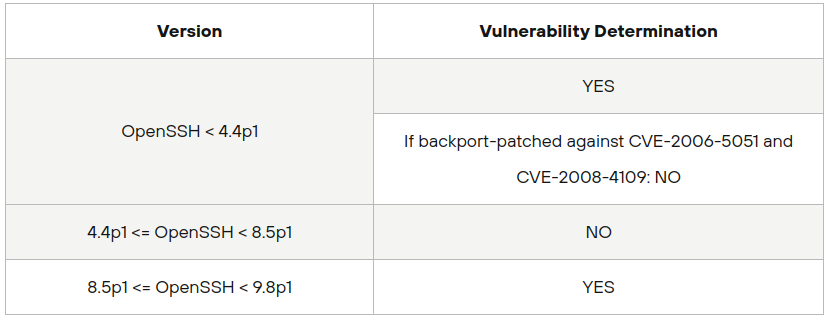
OpenBSD systems are not vulnerable due to their use of an async-signal-safe version of syslog(), which mitigates the race condition.
To protect against the regreSSHion vulnerability, it is recommended to:
If you cannot apply the patch immediately, consider the following workarounds:
LoginGraceTime to 0 in the OpenSSH configuration file. This eliminates the vulnerable window but may lead to denial of service by exhausting all available connections.sshsigdie function in OpenSSH source code and recompile.As of July 2, 2024, there is no known activity in the wild exploiting this vulnerability. While proof-of-concept (PoC) code exists, it has not been successfully used to achieve remote code execution in testing environments. However, the potential for targeted attacks remains, and organizations are urged to apply patches and implement mitigation promptly.
The regreSSHion vulnerability in OpenSSH (CVE-2024-6387) underscores the critical need for rigorous regression testing and prompt security updates. By understanding the nature of this threat and taking proactive measures, organizations can mitigate the risks associated with this severe vulnerability and protect their systems from potential exploitation.
Stay informed and vigilant, and ensure your systems are updated to safeguard against this and other emerging cybersecurity threats.
Subscribe to receive new blog post from PureID in your mail box