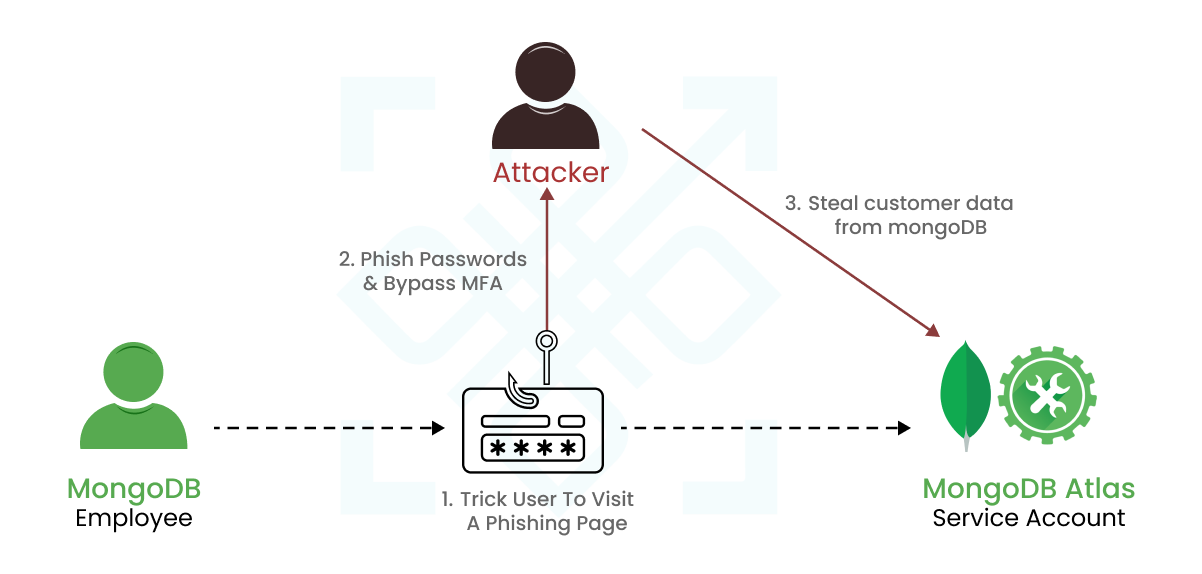
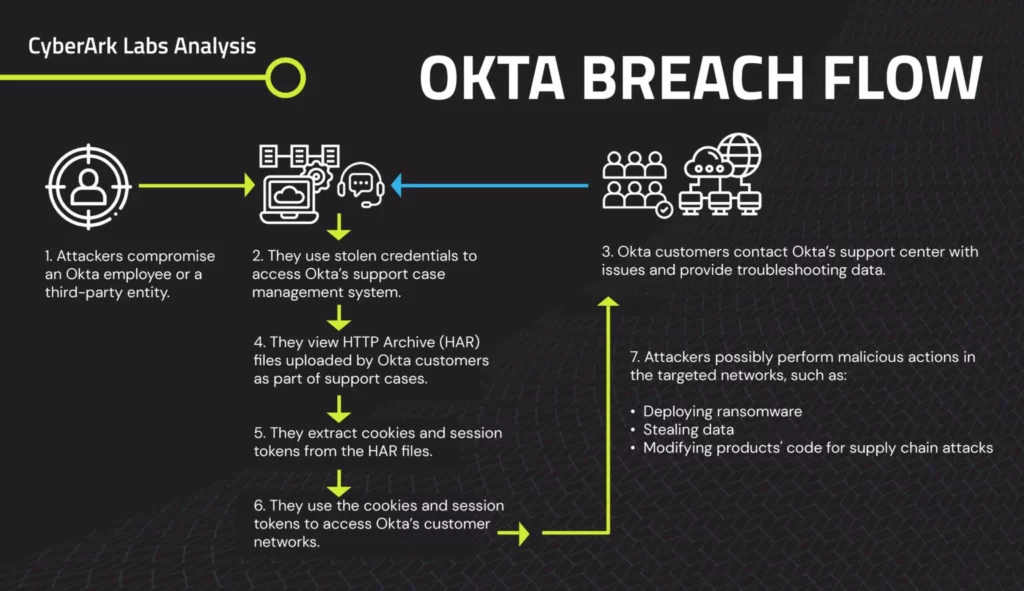
Introduction
In a recent disclosure, Microsoft unveils the details of a sophisticated cyber breach by Russian state-sponsored hackers. The breach, detected on January 12, sheds light on the tactics of the notorious hacking group, Midnight Blizzard, also known as APT29 or Cozy Bear.
Breach Overview: Understanding the Intrusion
In November 2023, Midnight Blizzard initiated a password spray attack. They compromised a legacy non-production test tenant account, gaining access to limited Microsoft email accounts.
Compromised Accounts: Impact on Corporate Email Security
The aftermath reveals that a select group fell victim, including members of Microsoft’s senior leadership team and employees in crucial functions such as cybersecurity and legal. The attackers exfiltrated emails and attached documents, putting sensitive information at risk.
Attribution and Interest: Identifying the Culprits
Microsoft’s threat research team attributed the breach to APT29, emphasising the group’s specific interest in Microsoft’s knowledge of their operations. This marks Midnight Blizzard’s return after their infamous 2020 cyberattack on SolarWinds.
Highlighting the Key Issue: Addressing Problems with Passwords
The breach underscores the vulnerability posed by traditional password systems. The password spray attack exploited weak passwords, showcasing the critical need for organizations to evolve towards passwordless solutions to enforce security.
Risk Mitigation: Addressing Future Threats
Microsoft, quick to respond, is now advocating for the adoption of passwordless solutions as a preventive measure against such breaches. The urgency to reassess and enhance cybersecurity measures has never been more evident.
Immediate Response: Microsoft’s Swift Action
In response to the breach, Microsoft has promptly applied enhanced security standards to its legacy systems and internal business processes. This immediate action aims to sabotage potential follow-up attacks and protect against further unauthorised access.
Ongoing Investigation: Collaborating with Authorities
The investigation is ongoing, with Microsoft actively collaborating with law enforcement and regulators to comprehensively assess the full impact of the breach. This collaboration is crucial for determining additional preventive measures and addressing the evolving landscape of cyber threats.
Conclusion: Looking Ahead
As companies face ever-changing online risks, the Microsoft hack is a clear signal that using weak passwords can be a big problem. Implementing passwordless solutions stands out as a critical step towards a more secure digital future.